Play with Python Projects Easily Using uv: From Installation to Running, All in One Step!
Python is a magical programming language with countless fun open-source projects behind it, such as AI tools, video processing scripts, and more. However, for many non-programmers, the biggest hurdles to downloading and running these projects from GitHub are "dependency management" and "version management."
Pip, pyenv, venv, poetry, conda... Just hearing the names is dizzying, let alone struggling for hours without success. The good news is, there's a new tool called uv that is simple, fast, and reliable, especially suitable for beginners. Today, I'll guide you step-by-step to try uv, from installation to running a project, ensuring you can get started right after reading!
1. Installing uv on Windows: Done in Two Minutes
First, we need to install uv on your Windows computer. Don't worry, no complicated operations are needed; just follow along.
- Download and Install:
- Start Menu - Find Windows PowerShell (right-click and select "Run as administrator" for more safety).
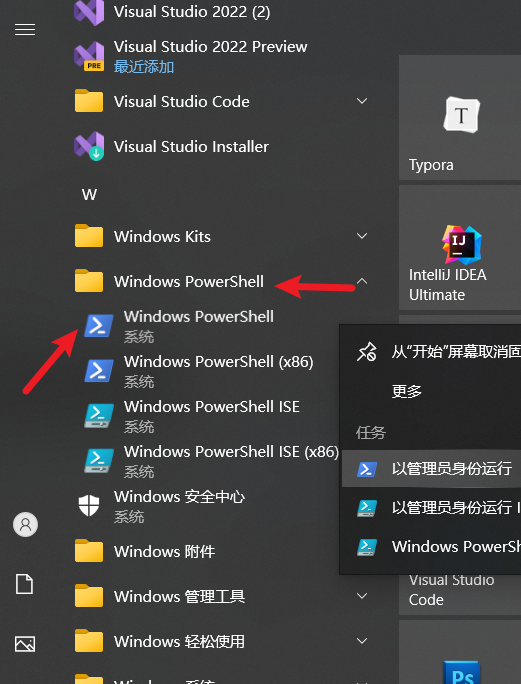
- Copy this command, paste it in, and press Enter:bash
powershell -ExecutionPolicy ByPass -c "irm https://astral.sh/uv/install.ps1 | iex" - This command will download and automatically run the installation script from the uv official website. The process takes from a few seconds to a minute or two, depending on your internet speed. Upon completion, the command line will prompt something like "uv installed successfully."
- Verify the Installation: Type
uv --version. If it shows a version number like "uv 0.x.x," congratulations, installation successful!
After installing uv, it will quietly stay on your computer, ready to help you anytime. Next, let's use it to create a new project.
2. Creating a New Project: Specify Python 3.10, Fill in What's Missing
Subsequent commands can be run in either
CMDconsole orPowerShell. Simply clear the address bar in any folder, typePowerShellorcmd, and press Enter to open it.
Suppose you want to try an AI project, but it requires Python 3.10, which you might not have on your computer. The power of uv is that it can automatically download and set it up for you.
- Create a New Project Folder:
- Create a folder anywhere, like on the desktop, named "myai". Enter this folder and open the cmd console.
- Create the Project and Specify Python 3.10:
- Enter this command:
uv init myai --python 3.10 - uv will create a new project. If Python 3.10 is not on your computer, it will automatically download it from the internet (may take a few minutes) and generate a virtual environment in the folder (like an independent small room, serving only this project).
- Enter this command:
- Check the Results: The folder will have a few more files, such as
pyproject.toml(the project's "manual") and.python-version(recording the Python version you're using).
Now you have a clean project environment. Let's add something to it!
3. Adding, Removing, Updating Third-Party Modules: As Easy as Ordering Takeout
AI projects usually need some "third-party modules" (like toolkits for processing data). uv makes this as intuitive as ordering takeout.
- Add a Module:
- Suppose the project needs
numpy(a mathematical computing tool). Enter:uv add numpy - uv will add
numpytopyproject.tomland download/install it into the virtual environment, done in seconds.
- Suppose the project needs
- Remove a Module:
- If you think
numpyis unnecessary, enter:uv remove numpy - It will be removed from the project, clean and tidy.
- If you think
- Update a Module:
- Want the latest version of
numpy? Enter:uv add numpy --upgrade - uv will check for the latest version and update it, saving you from manual checking.
- Want the latest version of
These commands automatically keep project dependencies consistent, so you don't have to worry about version conflicts. Next, let's try running a Python file.
4. Running a Python File: One-Click Launch
Suppose you wrote a simple test.py in the project, with content printing "Hello, AI!":
print("Hello, AI!")Directly enter:
uv run python test.py"Hello, AI!" will appear on the screen. uv will automatically run it using the Python 3.10 environment in the project, saving you the trouble of activating the environment. If the file has dependencies (e.g., using numpy), uv will also ensure they are in place.
5. Cloning and Running a Project from GitHub: Taking pyvideotrans as an Example
Now, let's try downloading a real project from GitHub, like pyvideotrans (a video translation tool, address: https://github.com/jianchang512/pyvideotrans.git), then configure and run it using uv.
- Clone the Repository:
- First, install Git (go to
https://git-scm.com/downloads/winto download, and click "Next" all the way during installation). After installation, you need to reopen the PowerShell or cmd terminal. - In the PowerShell or cmd terminal, enter:
git clone https://github.com/jianchang512/pyvideotrans.git
- First, install Git (go to
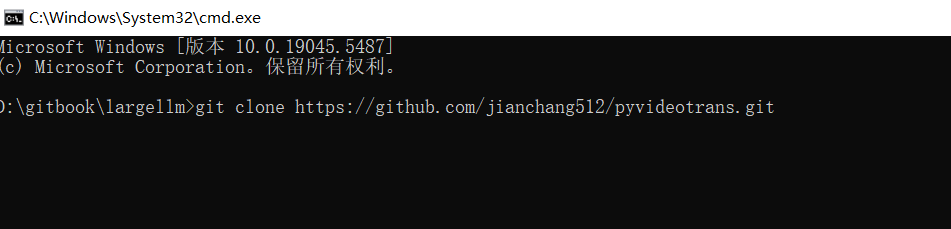
- This will download the project to the
pyvideotransdirectory under the current folder.
- Enter the Project Directory:
- Enter
cd pyvideotrans.
- Enter
- Initialize with uv and Specify Python 3.10:
- Enter:
uv init --python 3.10 - uv will check for Python 3.10 (download if not present) and create a virtual environment for the project.
- Enter:
- Install Dependencies:
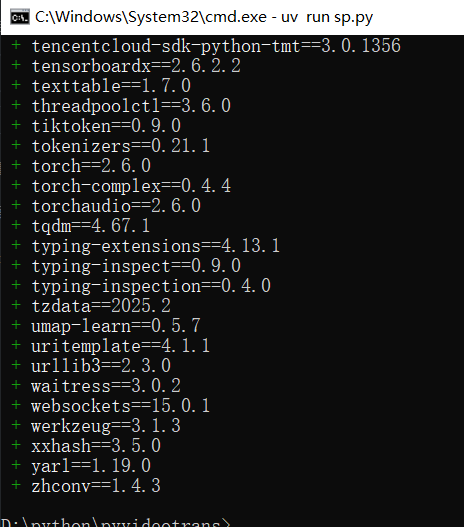
- The project comes with a
requirements.txtfile listing required modules. Enter:uv pip sync requirements.txt
- The project comes with a

- uv will install all dependencies according to this file, such as
torch,requests, etc. torch is large and may take a while.
- Run sp.py:
- Enter:
uv run sp.py - If everything goes well, the project starts! You can follow its instructions to try translating videos.
- Enter:
Isn't the whole process simple? uv hides complex dependency management behind the scenes; you only need a few commands to get things done.
6. uv's Major Features and Common Commands: A Summary
uv is an all-rounder, especially suitable for people like you who enjoy tinkering with GitHub projects. What's so great about it?
- Ultra-Fast Installation: 10-100 times faster than traditional tools (like pip).
- Environment Management: Automatically creates virtual environments; no manual activation needed; specify whichever Python version you want to use.
- Dependency Management: Supports
pyproject.tomlandrequirements.txt; adding, removing, and updating modules is one-click. - One-Click Running: Use
uv runto directly run scripts without worrying about environment configuration.
Common Command Quick Reference:
uv --version: Check uv version.uv init project_name --python 3.10: Create a new project and specify Python version.uv add module_name: Add a module.uv remove module_name: Remove a module.uv pip sync requirements.txt: Install modules from the dependency file.uv run file_name: Run a Python file.
